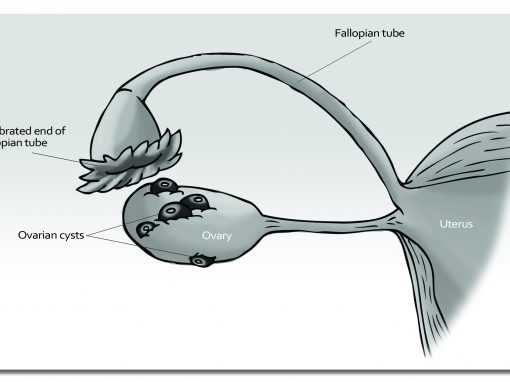
Fertility drugs may not be for everyone. Some women have to stop taking them because their ovaries have become hyper-stimulated (a severe health-threatening condition) or they have developed other problems such as cysts. Mother Nature has also provided us with a plethora of alternatives that yield fewer potential risks and side effects to choose from. Here are some of the more popular Herbs and Superfoods used for women’s health.
Vitex Agnus – Castus – (Chaste tree/berry) fruit
Vitex exerts a balancing action on the female sex hormones. Research has revealed that vitex affects the diencephalon-hypophyseal system. Here it causes increased luteinising hormone (LH) production and inhibits the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This leads to a shift in the ratio of oestrogens to progesterones, in favour of progesterones and hence a corpus luteum hormone effect.
What is obvious is that this herb is more phyto-progesteronal than oestrogenic and that it is more effective in troubles building up to menstruation, rather than starting with or following it, which points to an effect in support of, or mimicking, corpus luteum (thus, is a promoter of prolactin). Symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS) that respond well to chaste tree include reduction in headaches; pressure and tenderness in the breasts; bloating; acne; carbohydrate cravings; oedema (fluid retention); irritability; and mood fluctuations.
New research challenges the conventional wisdom that vitex can increase prolactin production. It is now known that vitex has Dopaminergic activity, which can explain its success in treating numerous gynaecological conditions, many of which may be related to high prolactin levels. Dopamine and compounds of similar molecular structure inhibit prolactin secretion from the anterior pituitary. Increased prolactin inhibits corpus luteal development, thereby indirectly reducing the secretion of progesterone in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, vitex may increase progesterone by reducing prolactin rather than by increasing LH as past research suggests.
Vitex, also known as ‘monk’s pepper’ can suppress testosterone levels, thus having an anti-aphrodisiac (decreased libido) effect; so if you are looking for some hanky-panky best not to over do it with Vitex. Prior to ovulation, vitex can assist with ovary maturation, combined with herbs such as blue cohosh (caulophyllum thalictroides), chaste tree works in a similar manner as medical drugs like Clomid (but without the long list of side effects) to enhance conception by stimulating ovulation of the ovum/s, (eggs). Vitex supports the release of gonadotrophins from the pituitary gland and decreases the symptoms of dysmenorrhoea (menstrual period pain).
It is recommended to avoid vitex during pregnancy (except under practitioner supervision) as it interacts with various endogenous hormones. Chaste tree lengthens the duration between periods if irregular, restores regularity in those afflicted with endometriosis and helps to alleviate menorrhagia (heavy menses) and secondary amenorrhea (absence of menses) (especially where due to a luteal phase defect).
Vitex may benefit during menopausal change and assist the body in regaining a natural balance after childbirth and after the use of the birth control pill. Vitex is recognised as a hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis regulator, but caution should be exercised in women under 20 years of age when hypothalamic-pituitary axis is easily disrupted.
Vitex also has a galactagogue action, which means it promotes the production or flow of breast milk. Other conditions vitex has application for include: benign breast disease; cystic hyperplasia; post-natal depression; endometriosis; fibroids; follicular/ovarian cysts; latent hyperprolactinaemia; luteal phase complaints; metrorrhagia; infertility resulting from decreased progesterone levels; corpus luteal insufficiency; threatened miscarriage; and dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Investigations into vitex have indicated that, if it is taken in high doses early in the menstrual cycle it may potentially suppress ovulation, though other investigations state that the use of vitex can actually assist in the ovulation (egg release) phase of the cycle and increase luteinising hormone levels.
When vitex is taken during the luteal phase (after ovulation) it may help to regulate and lengthen the cycle. This action can benefit an implanting embryo to give it a better chance of taking to the uterine wall. Vitex is relatively slow acting therefore it may take several months of use before optimal effects occur.
Chamaelirium Luteum – (False Unicorn Root, Helonias)
False unicorn root is one of the most highly reputed female reproductive system herbal medicines (though, the lack of in-depth phyto-chemical research and quality clinical trials is still required to fully appreciate false unicorn root’s therapeutic applications). What is known of this herb is that it exerts a menstrual cycle regulation effect, is a uterine tonic, and improves the secretory responses and cyclical functions of the ovaries; it appears to have an adaptogenic effect on this organ.
It contains phyto-oestrogenic precursors and thus is beneficial for conditions that require oestrogen normalisation such as in menopause. Hedonias is also known to be diuretic, a digestive tonic, and anthelmintic (eliminates parasites). False unicorn root is used for infertility caused by dysfunction in follicular formation.
The list of therapeutic applications that helonias could be applied to include: adenomyosis; amenorrhoea; anorexia; cystic hyperplasia; digestive weakness; dysmenorrhoea; endometriosis; fibroids; infertility; chronic pelvic inflammation; leucorrhoea; symptoms of menopause; menorrhagia; menstrual irregularity; threatened miscarriage; erratic ovulation; polycystic ovarian syndrome; nausea in pregnancy; to prepare the uterus for labour during pregnancy; dysfunctional uterine bleeding; post-partum haemorrhage; weight loss, corrects sexual debility; and sensations of downward pressure in womb.
False unicorn root is almost extinct in the wild because of excessive collection. So its use should be restricted until cultivation occurs. (Paeonia Lactiflora may prove a suitable and cheaper substitute).
Aletris Farinose – (True Unicorn Root)
True unicorn root is a bitter tonic digestive herb and it is a uterine tonic. This herb combines well with false unicorn root and its used in dysfunctional uterine bleeding conditions. Other applications for this herb may include: ‘idiopathic’ infertility; anorexia; cystic hyperplasia; digestive weakness; flatulence; and pelvic congestion.
Angelica Sinensis – (Dong Quai, Dang Gui) root
Dong quai is considered one of the ‘Emperor’ remedies for its ability to restore blood, regulate menstrual rhythm and strengthen the uterus. In China, it has been used for more than 2,000 years, and is referred to as female ginseng.
It builds blood the way astragalus (Huang Qi) builds Qi, bringing warmth and nourishment to the viscera as well as the skin, muscles and flesh. By quickening the blood, it banishes cold, wind, and dampness.
Dong quai benefits the liver, heart, spleen, and drives away the pain of obstructive stagnation (e.g. blood clots). Dong quai strengthens immunity and benefits the circulatory system. Research shows it increases utilisation of oxygen in the liver, calms the central nervous system and relieves pain associated with neuralgia (nerve pain), ischemia (lack of oxygen), and rheumatic or osteoarthritis. Due to its ability to nourish blood and mobilise circulation, dong quai promotes the healing of wounds, ulcers, and inflammations. The remedy possesses immune-regulating properties and may be used for acute viral infections such as colds and influenza.
Dong quai had been used to assist fertility for many hundreds of years in traditional Chinese medicine, and is said to regulate uterine function by stimulating smooth muscle, compounded by a complementary relaxing influence possibly associated with dysmenorrhea (painful periods – particularly of a dragging-down nature); amenorrhea (no menses flow); scant menstrual flow; abnormal menstrual cycle; moderate uterine bleeding; PMS; infertility; and menopause symptoms.
Clinical studies using a combination of herbs including dong quai, corydalis, white peony, and ligusticum wallichii demonstrated a 93 per cent improvement rate for treating dysmenorrhoea. In another study, infertility resulting from tubal occlusion was treated for up to 9 months with uterine irrigation (douche) of dong quai extract. Nearly 80 per cent of patients regained tubal patency, and 53 per cent became pregnant. Male infertility has improved with dong quai, sperm motility and viability both increased with its use. Dong quai also helps to alleviate liver disorders, lung problems, and it potentates Vitamin E activity. Dong quai can also be applied in conditions such as digestive weakness and allergies (sensitivities).
Dong quai contains many nutrients, such as: cobalt; copper manganese; calcium; potassium; Vitamin E; Vitamin B12; plant sterols; coumarins; essential oils; and various flavonoids. The plant-sterols in dong quai are in one way as powerful as animal-based estrogens, but they can pack enough punch to give it a dual effect in the body.
The herb can lower excess oestrogen activity in some women, while stimulating oestrogen activity in those who need it, resulting in a balance in both groups. The plant sterols in dong quai weakly mimic oestrogen in the body and trigger competition among oestrogen tissue receptors, resulting in a diluting effect.
In women with low oestrogen, the active constituent combines with women’s naturally occurring hormone to activate oestrogen receptors that otherwise might not be stimulated. Correct oestrogen balance is required for enhanced sexual responsiveness. The essential oils in dong quai have anti-spasmodic properties; studies using dong quai have shown that its pain-killing effects in reducing menses pain were measured at 1.7 times the effect of aspirin medication. These properties would also be applicable in other cases where mild pain relief is requires such as headaches and arthritis.
Dong quai has also been used for allergies; anxiety; water retention; mood swings; fibrocystic breast disease; poor circulation; and high blood pressure. Dong quai has an effect as a mild ‘blood thinning’ agent and should not be used during very heavy periods and when taking certain IVF or prescription blood thinning medications such as warfarin.
Paeonia Lactiflora – (Paeony, white Peony, Bai Shao) root
Paeonia is a wonderfully diverse herb primarily used in Chinese medicines for at least the last 1,500 years and is one of the top herbs used in female infertility and reproductive system disorders. Paeonia is an anti-spasmodic /mild skeletal muscle relaxant, soothes smooth muscle spasms, especially useful for dysmenorrhoea, angina, and migraine headaches. In traditional Chinese Medicine, it is considered as a blood and Yin tonic and is used to help ‘blood deficiency’. It is mildly ‘phyto-oestrogenic’, and exerts anti-convulsant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, immune and cognitive enhancing actions.
Various applications that peony may be used for include: anaemias; menstrual dysfunction; infertility; leukorrhea; uterine bleeding; spermatorrhea; neurasthenia; muscle cramps; epilepsy; polycystic ovary syndrome (in combination with liquorice); fibroids (in combination with pareunia suffruticosa, poria cocos, cinnamomum cassia, and prunus persica); endometriosis; androgen (hormone) excess; benign breast disease; irritable bowel syndrome; poor memory and concentration; ringing in the ears; dizziness; blurred vision; hot flushes; night sweats; menorrhagia; metrorrhagia; threatened miscarriage; myalgia; erratic ovulation; toxaemia; and restless foetus in pregnancy.
Peony is also a regulator of the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis and is a good substitute for other herbs like false unicorn root and shatavari. Traditionally, paeonia was also one of the herbs used to make a famous women’s tonic remedy called ‘Four Thing Soup’ together with rehmannia (rehmannia glutinosa), chuan xiong (ligusticum wallachii) and Chinese angelica (angelica sinensis). White peony builds Yin blood, women who have excessive mentration can enter a chronic cycle of anemia. By activating the spleens ability to get food broken down in to energy the women can build more upright chi. Latest studies show that a vital spleen helps to break down the nutrients we need from out food, especially iron. One of the keys to healthy blood appears to be the refreshing the iron ions inside the red blood cells. In Wicca (pagan witchcraft) tradition peony is used to protect the soul, body and spirit – worn on the body is said to promote fertility, love, luck, removes hexes and prosperity.
Cimicifuga Racemosa – (Black Cohosh, Sheng Ma) root and rhizome
Black cohosh is a popular herb used to normalise the female reproductive system. It is effective in the treatment of dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, menopausal symptoms, cramps, ovarian dysfunction and insufficiency. Traditionally it was employed for uterine and rectal prolapse, relief of spasms, sciatica, tinnitus, rheumatism and osteoarthritis. Black cohosh has a tonifying effect on the uterus and allays nervousness and coughing. More commonly used to help soothe the symptoms and depression of menopause, black cohosh does have its place in treating conditions that may contribute to infertility, some of which may include: hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis dysfunction; fibroids; endometriosis; polycystic ovarian syndrome; and idiopathic infertility. In TCM, black cohosh raises the Yang Qi, having an energetic lifting effect. Black cohosh has also been shown to have potential applications in male infertility. The viability of sperm cell and motility increased with the use of this herb.
*NOTE: Due to black cohosh’s emmenagogue action that may increase the strength of uterine contraction it is not recommended to be used in the early stages of pregnancy. *if required to use only under practitioner supervision.
Asparagus Racemosus – (Shatavari, wild asparagus root)
Shatavari is another of the prime rejuvenating (rasayana) Ayurvedic herbs, possibly the number one recognised female herb in ayurvedic medicine. It is considered particularly helpful in conditions affecting both the female and male reproductive systems. Shatavari is reputed as an aphrodisiac and promoter of fertility, which is said to ‘give the capacity to have a hundred husbands’.
One of its names means ‘having one hundred roots’, which also bespeaks its reputation as a fertility-enhancing plant.
Shatavari has notable nutritive properties and is excellent for nursing mothers to encourage the quantity and quality of breast milk (galactagogue), during pregnancy it may assist with increasing prolactin production. Preparations based on shatavari are often recommended for threatened miscarriage and improving circulation to the pelvic region. Shatavari is also used as a digestive aid (particularly as an anti-diarrhoea agent). It exerts a cooling action useful for condition such as heartburn; irritable bowel syndrome; hot flushing; menopausal symptoms; vaginal dryness, frigidity, PMS; irritability; cystitis; and recovering after illness. Shatavari is high is saponin compounds. In chinese medicine (TCM), shativari is considered a premier kidney yin tonic to support jing energy. It is also called the ‘flying herb’ for its ability to lift your vision, mind (noortropic and anti-stress brain tonic), and is said to gives you flying dreams (levity).
Caulophyllum Thalictroides (Blue Cohosh – Squaw root)
Blue cohosh is an anti-spasmodic to the female reproductive system with a tonic effect on the uterus and fallopian tubes. Blue cohosh is well applied in combination with other herbal medicine, for example, vitex agnus castus to assist with the promotion of ovulation and other herbs where uterine weakness; false labour pain; menopause; dysmenorrhoea; fibroids; amenorrhoea; ovarian/pelvic inflammation; and uterus atony are indicated. Like black cohosh, this herb also has emmenagogue and oxytocic actions, therefore should be best avoided in the early stages of pregnancy. Traditionally, blue cohosh was used throughout pregnancies to help prevent threatened miscarriages, but I would be conservative and remain cautious in using blue cohosh too early in the pregnancy. Blue cohosh may also help with oxytosin release.
Lepidium Megenii (Maca root; pepper weed; peruvian ginseng)
Maca is a rainforest herb that is a member of the cruciferous potato family. Maca is an important food in the diet of native Peruvians and is believed to have been used as a medicinal food for more the ten thousand years. It is rich in amino acids, high in proteins, calcium, magnesium, potassium and other nutrients. Maca root has been referred to as Peruvian ginseng and like other ginseng herbs; maca is known to increase energy and supports the immune system. Maca root is a super rich source of glucosinolates, which are known to be highly protective of carcinogens or cancer-causing agents. Maca is reputed to be very supportive in treating for stomach cancer.
Maca has been used therapeutically for: anaemia; chronic fatigue syndrome; increasing stamina; stress adaption; impotence; improving ejaculate volume; memory; osteoporosis (promotes bone desity); menopausal and menstrual problems. Maca has been shown to influence the hypothalamus-pituitary axis, thus influencing the endocrine system function. Studies have discovered that maca can increase progesterone and testosterone levels in women, making it potentially useful in luteal insufficiency (short-luteal-phase dysfunction).
In Ayurvedic medicine, maca root is regarded as a ‘rebuilding tonic’, strengthening the nervous system and brain via its effect on kidney energy. Harmonising of all endocrine functions and enhances emotional stability. There are various colors of Maca, white, red and black are commonly used. Red is thought to be the most nutritionally rich of all maca types due to the rich mineral content. Red maca is believed to best suit the ladies and black maca for male genitalia health. Maca can be sourced in raw, gelatinized, dual ext forms. Dosage: 5 to 30 grams daily.
Entada phaseoloides (Matchbox Bean)
Australian Aborigines use the seeds to treat female sterility and indigestion, and as a painkiller.
Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is another panacea for health and longevity seekers. Worker bees make this exotic substance for their queen bee, and all of us want to be queen or king bees of course. The amazing size, fertility, and life-span of the queen bee is attributed to its dietary food source of royal jelly. Royal jelly is definitely an energiser. It is high in certain unique fatty acids, simple carbohydrates, and pantothenic acid, which is supportive of the adrenals. It also contains the other B vitamins especially Vitamins B1, B3, B5, all of the essential amino acids, and many minerals, such as iron, calcium, silicon, sulphur, and potassium. Royal jelly has been used to support weight loss, as it is a rich and energising nutrient yet low in calories (20 calories per teaspoon), and to treat problems such as fatigue; allay body aches; boost adrenal gland function; relieve insomnia; digestive disorders; infertility; ulcers; and cardiovascular ailments.
Whether this mysterious substance really is a great rejuvenator and supporter of youth and longevity will need to be studied. But many people, especially women, experience an uplifting feeling when they take either liquid or encapsulated royal jelly.
Glycyrrhiza glabra (Liquorice root)
Liquorice likely has the most celebrated herbal past, extending thousands of years, beginning in the Orient and progressing around the world. It has many actions and clearly many uses. Also known as sweetwood or sweetroot, the ‘great detoxifier’, and the ‘great peacemaker’, this root contains many steroidal-like chemicals related to adrenal and ovarian secretions. Historically it was used for colds and coughs, and it has become popular as a laxative and for use in children, who tolerate its sweet flavour more readily than bitter herbs, with problems such as fever, colds, and constipation. Liquorice root has many apparent actions. It is an antitussive and expectorant, anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic, antitoxic (through liver support and protection) and antibiotic, possibly anti-cancer (recent research has shown liquorice’s inhibitory effect in some tumour growth), and a laxative. It also acts as a demulcent and emollient, meaning it softens and soothes tissues and mucous membranes. Liquorice further offers adrenal support with its mineralocorticoid-like substances and contains estrogenic chemicals such as beta-sitosterol and stigmasterol. Its adrenal stimulation allows it to be an anti-stress herb and to be helpful in inflammatory problems, such as arthritis, and in hypoglycaemia, which is a problem related to weak adrenals.
The estrogenic support allows its use in women as a sexual and uterine tonic and for problems of infertility. A study combining liquorice and white peony over 24 weeks using equal amounts of 6 grams of the herbs daily successfully treated women with infertility due to poly-cystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS); many of the women were recorded at the 12-week mark as being positively diagnosed pregnant. Serum levels of testosterone and free testosterone were significantly decreased after 4 weeks in 90 per cent of the women, and 25 per cent had fallen pregnant within 12 weeks of the 24-week trial. However, testosterone levels after 12 weeks were lower only in the pregnant group. At the end of the 24-week trial, the LH/FSH ratio was significantly lower in the treated group.
Liquorice root has been used as a stomach and intestinal remedy for problems such as indigestion; nausea; constipation; for infections of the respiratory tract, including colds and flu; hoarseness, sore throat and wheezing; hepatitis; ulcers; haemorrhoids; skin problems; muscle spasms and fevers associated with sweating; and general weakness. Liquorice has also been suggested for people with high blood pressure, yet there is a concern here since excessive intake can elevate blood pressure. It appears that the whole root or deglycyrrhizinated liquorice (DGL) is safe and has the positive attributes of liquorice extract without side effects. DGL has been the subject of recent interest and research, and it apparently still helps in healing ulcers. Usually liquorice root is used in herbal combinations and not by itself; it also balances the flavour of these formulas. In Chinese herbology, liquorice is one of the most commonly used herbs, along with ginger.
Barley grass
Barley grass helps to boost energy levels. The chlorophyll found in barley grass assists the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. It is a rich source of vitamins; minerals; amino acids; antioxidants; chlorophyll; beta-carotene; SOD (super oxide desmutase); and live enzymes. SOD found in barley grass helps the body detoxify chemicals and foreign substances, thereby helping to prevent the onset of disease.
Rice Bran Solubles Stabilized rice bran is one of the world’s great superfoods; hypoallergenic protein, rich in B and E complex vitamins and fibre, a source of omega 6 and 3 fatty acids, contains trimethylglycine (TMG), CO Q 10, alpha lipoic acid, mixed carotenoids, lecithin, ferulic acid, gamma-oryzanol, minerals, polyphenols, and IP6. Rice bran should be included as part of your fertility and wellness diet.
Chlorella algae (cracked-cell)
Chlorella is the highest known souce of Chlorphyll that detoxifies and protects the bodies cells. It is ranked among the highest nutrient dense superfoods known. It is high in a unique complex called Chlorella growth factor (CGF) and nucleic acid that is important for DNA and RNA in the body. Chlorella is also 50% protein. Chlorella is a green-algae and is one of the oldest known species on the planet and can reproduce 4-8 times a day, making it a sustainable nutrient source. Chlorella is rich in the cartenoids beta-carotene, alpha-carotene and lutein. It is abundant in health fats like oleic acid, vitamins B, C, D, E, K and contains the minerals phosphorus, calcium, zinc, magnesium and iron. Chlorella has many health benefits some include: supporting healthy hormone function, cardiovascular health, immune boosting – enhancing Nk cell activity, interferon and interleukin-12 cytokines, supports normal liver function, detoxifies heavy metals, protects against the of chemotherapy / radiation and has anti-aging properties. Chlorella may also be the mythological ‘Manna’ the nourishment that sustained the Israelites after Moses liberated them from bondage in Egypt of the Exodus biblical story.
Similar ocean and water sourced super foods to may include:
Blue-green algae – its pigments support natural antiaging stem cell production.
Hydrilla vertillata – is also a contender for the world’s most nutrient dense plant. It may be the richest source and vegetable-based Calcium and Vitamin B12.
Marine Phytoplanktons -is possible the world’s most nutrient dense food source. Seaweeds are very nutrient dense and good sources of trace minerals and iodine.
Spirulina
“The future of nutrition is found in the ocean.” – Jacques Yves Cousteau.
Spirulina is a form of blue-green micro-algae rich in vitamins, minerals, chlorophyll, polysaccharides, sulfolipids, gylycolipis and protein. It is recognised as a whole food source. The concentration of nutrients in spirulina is like no other grain, herb or plant and is highly digestible and assimilative. Spirulina contains gamma-linolenic acid (GLA); linoleic acid and arachidonic acid; is a highly alkaline complete protein with all essential amino acids; Vitamins – A, B’s, B12, rich source of beta-carotein, also has vitamin C, E, and K. Minerals – potassium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron and magnesium; the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. Spirulina supplies all the necessary nutrients to cleanse and heal the body; the high protein content helps to stabilise blood sugars; reduce appetite; boost energy; reduce elevated cholesterol; protect the immune system; and enhance oxygen transport throughout the body. Spirulina also contains the antioxidant /polypeptide blue pigment Phycocyanin that can trigger production of stem cells.
Phycocyanobilin is coverted in the body into phyocyanurubin similary to bilirubin.
Wheat Grass
Wheat grass is another of the super foods and is an energy-packed food containing an immense array of over 100 vitamins, minerals, chlorophyll, laetrile, and other trace elements. Wheat grass is used to increase the health of the immune system; lower blood pressure; detoxify the liver, colon and kidneys; improves circulation; nourish and carry oxygen to the body cells; protect chromosome damage; rid the body of the toxic effects of pollution; and has potent antioxidant properties. The juice from wheat grass is a favourite among people who are into fresh raw juices and is a very supportive food source used by people combating cancers. Wheat grass has been linked to enhancing FSH production in the body, therefore improving the quality and protection of the eggs (ova) in the reproductive system; these early investigations have not been validated. Wheat grass is highly regarded in TCM for supporting fertility health.
Other Phyto-Medicines that may be considered for female infertility:
Anise (pimpinella anisum); viburnum opulus (cramp bark); diosceria villosa.spp (wild yam); glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice root); aloe vera; zingiber officinale (ginger root); anemone pulsatilla (pasque flower – use low dose, only with care); leonurus cardiaca (mother wort – use with care); capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse); ligusticum wallichii (cnidium; chuan xiong); nettle leaves; mitchella repens (squaw vine); alchemilla vulgaris (ladies mantle); ashoka (saraca indica); lamium album (white deadnettle); black haw (viburnum prunifolium); beth root (trillium erectum); mugwort (atremesia vulgaris – use with care); red raspberry leaf (rubus idaeus/r.strigosus); red clover (trifolium pratense); chamomile (matricaria recutita, chomomilla); snow peas; seabuckthorn (contains omega 3,6,9 nutrient dense may aid progesterone and DHEA), pine pollen (phyto-androgen superfood), schisandra berry (regards as one of the top chineses remedies, beauty tonic, aid hormone balance via helping liver detoxification – an all-in-one tonic is believed to affect all twelve meridian working on all five TCM elements and supplying all three treasures); goji berry (superfood that boosts growth hormone, aids recovery, repair and support of just about all bodily functions); longan berry (‘dragon eye’ – it calms the mind, relaxes, gives mood support, builds qi and energy, improves digestion and skin, and is a blood tonic); kacip fatimah (labisia pumila) is an all-round female tonic.
A TCM recipe called Nuzhen Yunyu Decoction (NYD) was studied by Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Academy of TCM, Beijing. The conclusions to the study showed NYD significantly improved reproductive system blood circulation. This promoted a holistic regulation of the reproductive system and enhanced ovulation. Bushen Huoxue Decoction has also been used to treat ovulation dysfunction.
Cassava root (Yuca, Tapioca), yams and okra leaves in West Africa particularly Nigeria (Igbo-Ora) are consumed regularly and are claimed to enhance the changes for multiple pregnancies (e.ge. twins). The birth rates in West Africa is almost four time higher than the rest of the world.
In Celtic / Norse (Druid) traditional healing these are some of the main herbs and plants used for fertility: agaric, birch, bistort, bodhi, carrot, chickweed, cuckoo-flower, cucumber, daffodil, dock, fig, geranium, grape, hawthorn, hazel, horsetail, mistletoe (*may be poisonous), mustard, myrtle, nuts, oak, olive, palm date, patchouli, peach, popy seed, rice, and sunflower petals.