‘The Silent Epidemic’ – The dark night of the soul
The secret society that no one want to be a part of
To firstly become pregnant and then to lose a child can be a soul-crushing ordeal to experience during a person’s life. For those who have sadly lost a child due to miscarriage, you will know the experience is a very unpleasant one and we all grieve and cope one way or another very differently depending on our beliefs and circumstances. The following information will hopefully shed some light about the reasoning behind why miscarriages may occur and what active measures that can be taken to minimise and potentially prevent miscarriages occurring in future conceptions.
A miscarriage by definition is the delivery of or the process of delivering a conceptus before there is a viable foetus. There are many different types of miscarriage that can occur, due to many different known and unknown causes. Here are some examples of the names used to describe the various types of miscarriages: threatened miscarriage; inevitable miscarriage; incomplete miscarriage; complete miscarriage; menstrual miscarriage; subclinical miscarriage; missed abortion; and recurrent (habitual) miscarriage.
- 1 in 5 pregnancies now ends in miscarriage
- 1 in 10 pregnancies now end in premature birth or ‘small for dates’
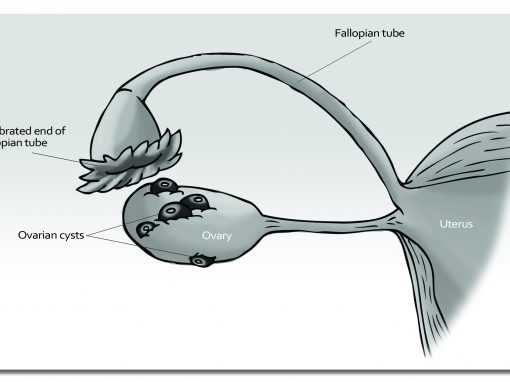
- 1 in 30 infants are born with congenital defects (despite apparent improvements in diagnostic techniques). The Miscarriage Association in the UK estimates the miscarriage rate may be as high as 1 in 3 or even 2 in 5.
- 1 in every 250 pregnancies is ectopic.
- The harsh reality is that 5 out of 6 embryos will not have survived out of 8 weeks gestation in the womb.
Each individual conception is uniquely a one-off prototype (in a sense), designed from a genetic blueprint that has never been tried before, therefore the struggle for life is fraught with many potential problems and complications that can go wrong within the microcosm of the human body.
Chances of miscarriage
Week 1-2 75 per cent pre-implantation, 30 per cent post- implantation
Week 3-6 10 per cent at 14 days post ovulation when hCG reaches 50-80
Week 6-12 5 per cent (or less if heartbeat heard)
2nd Trimester 3 per cent (considered stillbirth after 20 weeks)
3rd Trimester 1 per cent (after 24 weeks).
Miscarriage affects 12 to 22% of clinical pregnancies.
IVF and medical assisted fertility procedures have an increased miscarriage rate in comparison to natural occurring pregnancies.
The majority of miscarriages (75-90 per cent) usually occur during the first trimester of pregnancy before 13 weeks.
Causes of miscarriage are – chromosomal 10-50 per cent (increasing), anatomical defects 5-12 per cent, endocrine dysfunction (e.g. diabetes, thyroid imbalance) 10 per cent, immune coagulation 30-50 percent, and unknown 15-50 per cent.
Causes of recurrent miscarriage (from medscape review) – anatomic 10 per cent; chromosomal 10 per cent; endocrine (e.g. luteal defect; elevated LH, FSH, Prolactin) 20 per cent; and immune/coagulation 60 percent. Elevated levels of uterine natural killer cells (UNKC) white blood cells has shown to be a major contributing factor to a large percentage of recurrent miscarriages.
Causes of miscarriage can be found in 50%/50% in men and women.
Genetic/Chromosomal
More common in older women and men
Environmental toxin link including – radiation; free radical/ROS link in both eggs; and sperm. Down’s syndrome and Turner Syndrome are examples of chromosomal abnormalities. Wilson’s disease, a genetic condition affecting the liver, may also contribute to problems. Between 30 to 40 per cent of birth defects are caused by medical, environmental, genetic and psycho-social factors that could, to some degree, be prevented. Certain individuals that come from various cultural backgrounds are more prone to different types of inheritable diseases. People from ethnic or Eastern Jewish ancestry backgrounds have a higher likelihood to Tay-Sachs. In Latino and African American (or Negro descent), Sickle-cell anaemia. Caucasian white people to cystic fibrosis and people from Mediterranean, African, and Southern Asian tend to get thalassemia.
Apart from ethnic backgrounds that are linked to inheritable diseases, you may simply have a higher incidence of conditions such as autism or forms of mental retardation in your family, a specific gene that has been identified to contribute to these problems is the fragile X gene. Other forms of inheritable health conditions may include certain types of cancers, lung diseases, and neurological or neuromuscular diseases such as muscular dystrophy.
Our genes are like light switches that can be turned on and off depending on your life chooses – chemical, physical (structure dictates function), and emotional / spiritual. Disease is a genetic expression of chooses, be them known or unknown. Our genetic code (put simply) is made up of a sequence of a 4-lettered alphabetic code (A, G, C, T) (A is always paired with T, and G with C) A – adenine, T – thymine, G – guanine, and C – cytosine; that are randomly alternated along the genetic chain. When there is a glitch in the coding sequence (e.g. one or more of the letters are out of place) then this will result in a specific genetic defect determined by the position this code break is located. The human genome has been identified to have over 25,000 genes (a flee has 30,000 genes) on DNA chromosomes.
Each cell comprising a membrane (mem-BRAIN – receivers of self > nano frequency of white light – awareness that is turned into behaviour); liquid crystal; semiconductor with gates and channels; and fractal geometry – like a computer chip); 46 chromosomes, with 6 billion letters in this chemical alphabet genome. Each genome had encoded within it is the instruction manual to develop, diversify, and repair 70 trillion cells comprising the average adult sized body. The human genome makes over 200,000 different proteins (proteome). It is estimated that there are some 30 to 100,000 various species of bacteria in the human body equivalent to 2 million genes (microbiome inner-verse), 1.5 quadtillion bacteria on a human body. 100 times out numbering human genes.
Approximately 5 million species of fungi account for billions of genes. Viruses on earth est. 10 to the 31 (10 million times more that the stars in our universe) – symbiogenisis. 90-98% of your DNA is classifies as ‘Junk DNA’ (dark matter), science is still trying to understand it but it is believed that it coded from micro-RNA that switches the genes on and off and can leave the cell unlike messenger RNA and DNA. Nature wastes nothing, so with future advances in science the temporarily hidden knowledge of the full purpose of junk DNA will be revealed. Eighty-five (85) percent of our genes are utilised to build our brain. It is believed that a single gram of DNA can store at least 5.5 petabits or around 700 terabytes of data.
Scientists have recently discovered that the male Y-chromosome where many genetic defects are to found is not as weak and fragile as once believed. Studies have shown that this chromosome is actually able to self-repair by over laying or looping upon itself to regenerate. This is big news to geneticists and offers great hope, because Y-chromosome defects were previously thought to be incurable, but now there will be future research into decoding the genetic sequence and stem cell research. The science on the evolutional fusion theory of chromosome number 2 is still very wobbly and not conclusively proven?
These conditions may one day be a thing of the past with further investigations into this new era of medicine. Even though many of these afore mentioned genetic problems may not be a direct cause of miscarriage or infertility as such, they are important factors that are well worth knowing about. Science now believe that our genes don’t dictate our destiny, the expose zone (external environment and lifestyle choices) can influence and modify our gene expression. The human body is essentially a super meta organism or halobiont – an aggregation of different species of organisms and their collective genomes that work together to form a symbiotic ecology. The microbiota, mitochondria, immune system and environment all interplay with one another that dictate our adaptability and threshold tolerances. Science now understands that the vaginal bacteria pasted onto the baby during birth is essential for the baby’s immunity.
What is MTHRF?
This acronym stands for Methylene-TetraHydroFolate Reductase. It is an enzyme that converts the folate you eat into the active form that the body needs to use. The 2 main genes involved in this process are MTHFR C677T and A1298C. These genes require methyl groups to switch on and off the cells activites Methylation is required for these processes to function correcty. Methylation is the process by which your body transfers one set of atoms into a series of amino acids, proteins, enymes and DNA in each and every cell and tissue in your body. The MTHFR Gene – there is currently a total of 34 mutations in the MTHFR gene. The gene sits on chromosome 1.
There are two key variations of tests (at this stage). SNP’s that are currently tested are: MTHFR C677T and MTHFR A1298C. Heterozgous = 1 copy of the gene from either parent. Homozygous = 1 copy of the gene from each. MTHFR C677T Heterozygous = 40% loss of function; MTHFR C677T Homozygous = 70% loss of function. MTHFR A1298C Heterozygous = 20% loss of function; MTHFR A1298C Homozygous = 40% loss of function. MTHFR C677T and A298C compound heterozygous = 50% loss. A positive MTHFR mutation may identify that the immune and detoxification systems are not functioning optimally. In cases with of severe MTHFR gene defects, a developing fetus may suffer brain defects like spina bifida or anencephaly.
A defect in the MTHFR gene can cause an abnormally high homocysteine level in the blood are a result of poor methylation. This can potentially lead to other health conditions such as: cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, glaucoma, ischemic stoke, artherosclerosis, migraines, lethargy, hypothyroidism, impaired cognative function, mood / mental disorders – schizophrenia, bipolar, and depression.
Supplementation with Methyl folate 5-MTHF, Methylcobolamin (active B12), P5P activated B6, and Trimethylglycine (TMG, Betaine) may be recommended.
A personal observation – apart from surgical investigations such as laporoscopies, pre-conceptially the results from MTHFR gene tests next to the Anti-Mullerian blood test are the two most common pathology measures that cause great distress to women. Everyone is biochemially unique and there is much confusion over the ‘science’. The consequences of not adapting to the perceived stress I feel may be more detrimental then obsessively trying to troll over all the ingredients of your supplement’s futility pursuing the ‘perfect’ daily balance of ‘folate’ and other ideal nutrients. The worry may drive you crazy!